Digital Dentistry
Dental solutions have never been better – digital dentistry is paving the way for better oral health and, ultimately, a better you!
Digital dentistry has revolutionized the dental industry. Whether it is dental case assessments and diagnostics or faster and safer solutions to dental issues, digital dentistry has paved the way for more comfortable and better-suited prosthesis than ever before.
What Is Digital Dentistry?
Digital dentistry is the most basic concept of dentistry, simply upgraded thanks to technological involvement. It has allowed digitally controlled equipment and devices to produce faster and safer solutions in dentistry medicine. It has revolutionized how dentistry cases are assessed and addressed and opened many solutions for patients.
Digital dentistry is credited to French Professor Francois Duret, who invented the CAD/ CAM technology back in 1971. Since then, as technology has advanced, digital dentistry has grown tremendously, allowing dental practitioners to make better-suited and more perfect prostheses for patients.
Just a few years back, if you were to visit your dentist for any dental problem that required an accurate impression of your jaw, they were to use paste or a paste-like gooey substance. It would adhere to the surface of your teeth structure and jaw before hardening and taking the impression. The dentist would then remove it, conditioning your jaw to pain.
Removing the hardened paste was challenging, would leave the patient in pain, and cause gag reflexes to make the whole ordeal a lot more difficult. Fast forward to the digital dentistry age, and we have amazing new technologies that can carve every nook and cranny of your mouth for a perfect 3D representation of your jaw.
Dental Radiology and Imaging
Dental Imaging And Radiology In The Modern Day
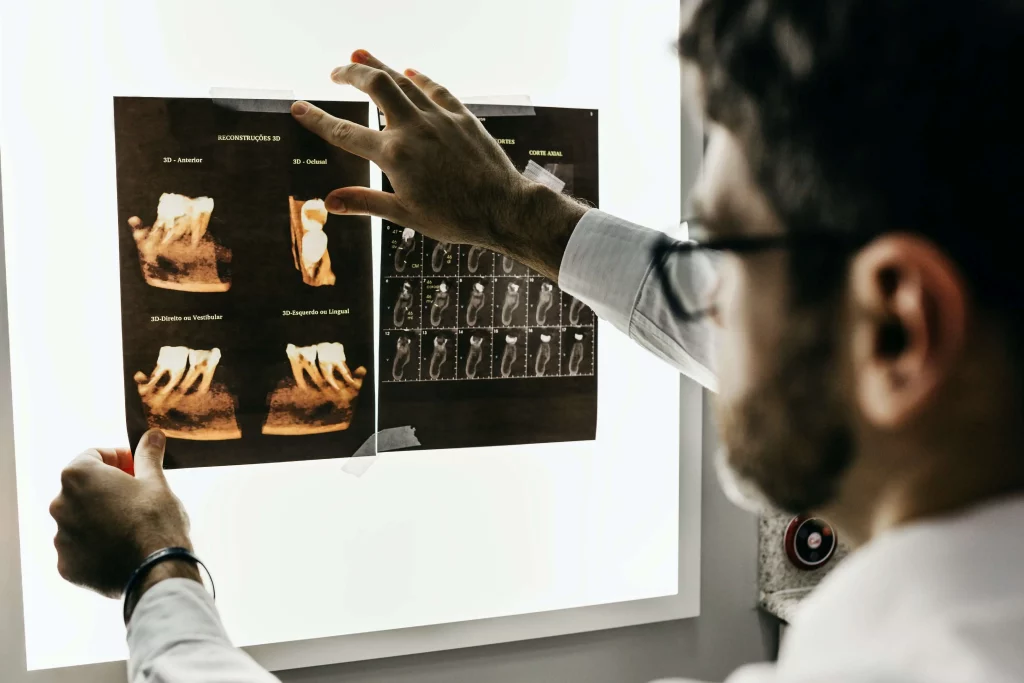
Dental imaging is of a few types and the most common among them includes X-Rays. In the olden days, X-Rays were painstakingly taken on X-Ray films and developed in dark rooms. As dental technology has evolved, we now have the convenience and utility of digital X-Rays.
Other than that, we also have Digital Volume Tomography, also known as DVT, which helps with more detailed dental imaging and treatment planning.
Both of these technologies and others have made it possible for dental treatment to be easy in recent years. Let us take a look at how each of these technologies can help us today:
Digital X-Rays
Digital X-Rays c a few types:
- Periodontal X-Rays – These X-Rays help to visualize 1-3 consecutive teeth, along with their roots and supporting gingiva.
- OPG – An OPG shows the entire dentition of a patient, including the maxillary sinuses and the temporomandibular joints.
- Bitewing X-Rays – These X-Rays show the crowns of the maxillary and mandibular teeth.
These X-Rays are used for the detection of dental caries, cysts, placement of fillings, bone loss, abscesses and even certain infections. These X-Rays can also help to determine the course of action of the treatment as well.
With the help of digitalization, dentists can now zoom in, zoom out, create high-contrast images and edit the image for better clarity. All of this will help to determine more precise treatment plans for the patient.
Tomograms
Tomograms are ideal for isolating a specific layer of the mouth. The image blurs out all the surrounding structures and layers. This type of imaging is ideal for examining structures that have an obstructed view due to the surrounding structures.
Digital Volume Tomography
DVT is used to generate high-quality 3D images of the bony structures in the oral cavity. DVT is the best diagnostic imaging technique to determine fractures and how to treat those fractures. Other than that, it is a great tool for planning dental implants as well.
DVT has many advantages over 2D X-Rays as the quality of images generated in DVTs is very high. Moreover, the 3D images generated in DVTs are also able to determine irregularities in the oral cavity much better than 2-D X-Rays.
DVTs are the diagnostic tool of choice for complex dental treatments. These also include issues in the head and neck regions of the body. They are also ideal for dental treatments that aim to improve multiple issues in the dentition of the patient.
MRIs
MRIs are commonly used for soft tissue evaluation in the oral cavity and surrounding regions. MRIs also generate 3-D images of the soft tissue structures in the head and neck, which help with precise diagnosis and effective treatment planning.
Conclusion
Dental imaging and radiology have evolved greatly to fit the needs of modern medicine. There are different types of imaging for all the different types of oral and dental concerns. Dental imaging and radiology have helped to make diagnosis simple and effective for doctors all over the world.
Digital Smile Design
Digital Smile Design is a digital diagnostic and therapeutic planning tool that develops a dentist’s capacity to diagnose, increases outcome predictability, and encourages collaboration between dentists and their patients. With Digital Smile Design (DSD), dental restorations are entirely based on an in-depth examination of the patient’s dental and aesthetic characteristics. DSD specialists may better understand how the teeth, gums, and lips interact with one another and how they connect to add to the aesthetic appeal of a patient’s smile.
How Is a Digital Smile Design Made?
While the integration of aesthetic factors differs by DSD software, the core technique for generating a smile design stays the same. Aesthetic design is possible with any DSD software by creating reference lines and patterns on the exterior and interior of the oral cavity through digital photos.
- Facial Analysis
For facial analysis, DSD tools use reference lines as a standard to determine the frontal image of the face. Reference lines are used in facial analysis to generate standard parameters for the face’s frontal aspect. Vertical lines locate the facial median, which traverses the chin, nose, and forehead. The inter-commissural and inter-pupillary lines provide a comprehensive perception of symmetry and a lateral view of the visually pleasing face.
- Intra-Oral Examination
The size of the top lip is measured in both relaxed and smiling state to assess the gum presentation. The smile curvature is determined by contrasting the interdental margins of the maxillary front teeth. The oral contours are determined by the dimensions of the bottom lip and the posterior-anterior curve of the teeth. The facial image is then edited to display the intra-oral image exclusively. The dentist can determine the required symmetrical changes by using the referential facial midline and intraoral image.
Benefits of Digital Smile Design
Digital designing and imaging make it easier for patients to see the desired outcome before the therapy begins, increasing the treatment’s predictability. The dentist can ease patients’ worries by graphically displaying the treatment’s result, inspiring and enlightening them about its advantages. Using aesthetic imaging of the patient’s condition in conjunction with a computerized examination of facial, dental, and gingival factors helps clinicians diagnose patients more accurately and develop treatment plans that are more standardized and realistic. DSD results in customized smile designs by boosting patient involvement, creating more visually appealing, empathetic, emotive, and self-assured smiles. Also, it gives patients a chance to compare the pre-and post-treatment situation and feel assured that their investment of time and money was worthwhile.
Cad/Cam In Dentistry
CAD / CAM means computer-aided design and computer-aided manufacturing.
Thanks to this technology, the age of digital dentistry has begun. The software and materials are increasing day by day and increasing the variety of prostheses made.
Until recently, the measurements taken in the mouth with classical measurement techniques were digitized in the laboratory and design and production was carried out. Since the measurements taken with digital scanner systems that can now be used in mouth do not contain transfer errors, they allow more error-free and faster production.
With the development of new software and materials, it is possible to make more comfortable and more aesthetic teeth by decreasing the margin of error as the production time accelerates in digitally produced prostheses.
With the CAD / CAM system, the treatments can be completed quickly, without being divided into too many sessions, in a short time depending on the prosthesis feature and even in a single day in many cases.
Instead of paste / paste-like substances that cause nausea reflex, the ability to measure teeth with intraoral scanning cameras provides a significant convenience for people who have difficulty in taking measurements due to gastric reflex.
Guided Implantology
Guided implantology is a contemporary way of inserting dental implants in individuals who are missing a tooth or have just gotten their tooth removed. This method uses computers to scan the persons mouth and create a three-dimensional model that allows us to plan the ideal procedure before performing it. Guided dental implant surgery involves using high-tech imaging tools and machinery to aid or ‘guide’ them to manufacture and insert dental implants more precisely, accurately and efficiently. Guided implantology is becoming increasingly popular in dental practices.
What Does Guided Implantology Involve?
The first step in guided implantology is to perform an oral examination of the patient to check whether implants are an appropriate treatment. We will first scan your mouth using a dental CBCT and three-dimensional imaging techniques to assemble two-dimensional images into a 3D digital model. A CBCT scan collects essential information, including the position of sinuses, nerves, and other points of reference. We then use this model to plan the procedure and prepare a surgical guide to place the implant. After we have placed the crown, you will see a natural-looking tooth.
Why Should You Opt for Guided Implantology?
While experienced dentists can perform an implant procedure to create an aesthetically appealing result without the help of a computer, guided implant surgery significantly lowers the risk of human errors by planning the most efficient, safest procedure with the best-looking outcome. In addition, guided implantology enables the dentist to superimpose abutments and how much space will be required for the crown and any other structure that is going to be added.