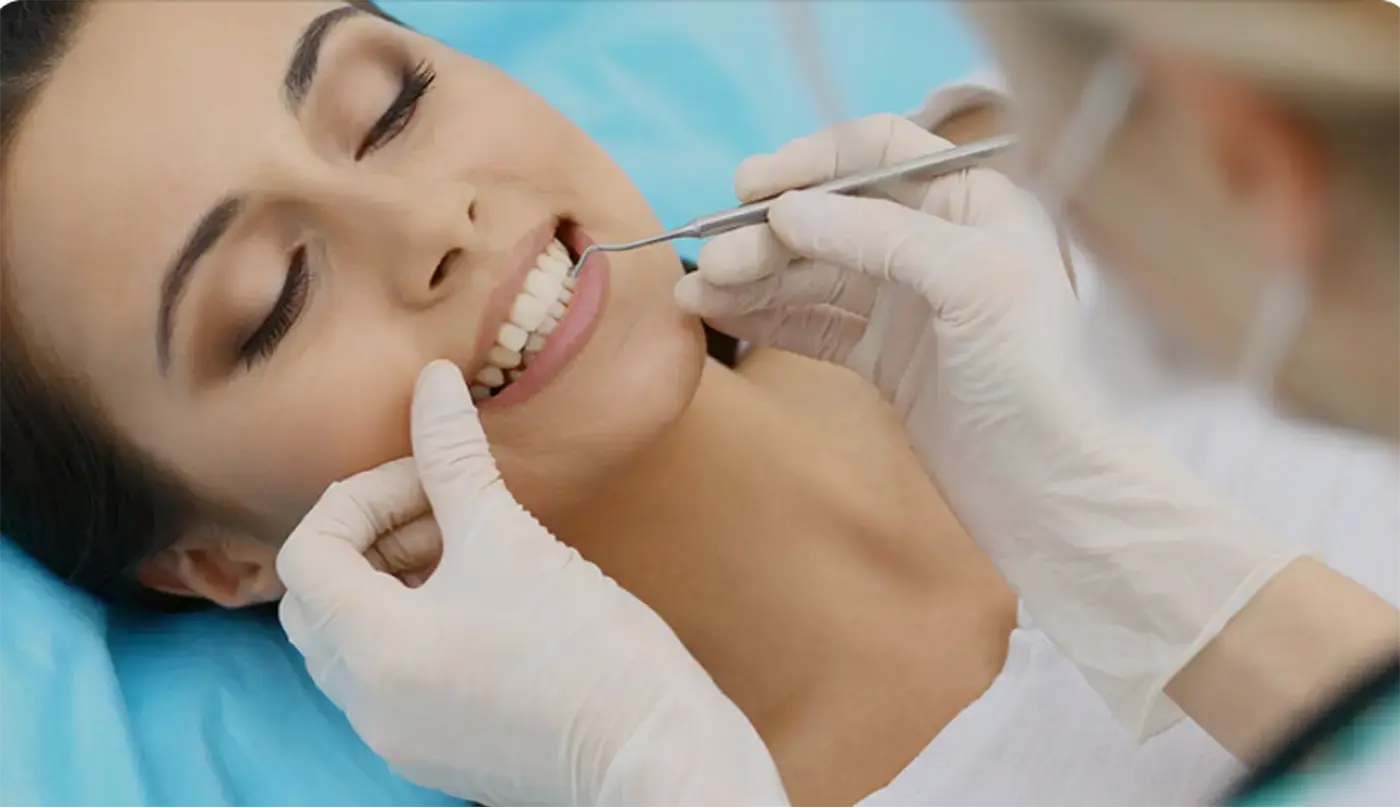
In dental practice, the thought of treatment can cause anxiety and concern for some patients, particularly those with dental phobia or those who require extensive dental procedures. In these situations, sedation can be a useful option to make the treatment process more comfortable and less stressful. In this article, we will take a closer look at sedation dentistry: What is sedation, who is it suitable for, what methods are available, what benefits it offers and what potential side effects need to be considered.
What is sedation in dentistry?
Sedation is a procedure in which patients are placed in a relaxed and anxiety-free state during dental treatment. The aim of sedation is to make the patient calm and co-operative so that the treatment can be carried out without fear or discomfort. Sedation can be administered at different levels – from mild sedation to deep sedation or even general anaesthesia – depending on the patient’s needs and the type of procedure.
Who is sedation recommended for?
Sedation dentistry is particularly suitable for:
– Patients with a fear of dental procedures or dental phobia.
– People with low sensitivity to pain.
– People with a high gag reflex.
– Patients who need extensive dental treatments that require longer sessions.
What methods of sedation are available?
Here are some common options:
- Oral sedation: before the procedure, the patient takes a sedative medication to help them relax. This method is particularly suitable for patients with mild anxiety.
- Intravenous sedation: a strong sedative is administered via an intravenous injection to achieve faster and more intense sedation. This method is often used for patients with moderate to severe anxiety.
- Nitrous oxide sedation: The patient breathes in a mixture of nitrous oxide and oxygen, which provides gentle sedation and pain relief. This is a good choice for patients with mild to moderate anxiety.
- Deep sedation and general anaesthesia: These deeper methods are usually performed in a hospital or specialised facility and provide intense sedation or even general anaesthesia for patients with severe anxiety or more complex dental procedures.
The advantages of sedation are manifold:
– Reduces anxiety and discomfort during treatment.
– Enables longer and more complicated dental procedures.
– Promotes co-operation between patient and dentist.
– Can help reduce the need for local anaesthesia.
– Improves the overall patient experience and contributes to a positive attitude towards dental care.
Potential side effects:
Although sedation is generally safe, it can cause some side effects, including:
– Nausea and vomiting
– Drowsiness and dizziness
– Headaches
– Loss of memory about the treatment
It is of great importance that the dentist informs the patient of possible side effects and ensures that the patient is suitable for sedation before it is carried out.
Conclusion:
The use of sedation in dentistry is a valuable option to help patients overcome their fear of dental procedures and provide a comfortable treatment experience. Through various sedation procedures, dentists can cater to the individual needs of their patients and ensure that treatment is effective and stress-free. It is important that patients discuss their concerns with their dentist and together choose the best option for their specific needs.